Ear Attic Defect

This is a cholesteatoma that has formed.
Ear attic defect. A cholesteatoma is an abnormal noncancerous skin growth that can develop in the middle section of your ear behind the eardrum. Wide transcanal atticotomy was performed and the bony defect was enlarged into the antrum and was packed and left open. It is our experience 1 that with staged cwu tympanoplasty the retraction pocket has already occurred and is observable at the time of the second stage operation. Residual attic and tympanic membrane defects were reconstructed with a composite tragal graft.
The majority 98 of people with cholesteatoma have ear discharge or conductive hearing loss or both in the affected ear. Reconstructing the attic defect is usually done with tragal cartilage with perichondrium as an island graft type fashion. A dark middle ear effusion is noticed in the middle ear. The area of the superior portion of the eardrum is retracted or sucked in trapping skin cells and debris and eating away at the hearing bones and ear canal bone.
Reconstruction of the attic mastoid defect ossicular chain reconstruction tympanic membrane repair. Depending on the defect size more than one piece of cartilage may be used. It may be a birth defect but it s most commonly caused. 1 through an attic defect 2 via erosions in the canal wall 3 as a pars tensa invagination and 4 as a borderline.
Bone defect of the attic wall eustachian tubal dysfunction and middle ear inflammation among others are proposed as factors that can cause the pocket. A serous effusion is present. Citation needed other more common conditions e g. 6 status post tubulation.
Attic retraction pocket cholesteatoma case 1. Group 2 included 31 patients with extensive disease within the mastoid cavity proper. Overt attic cholesteatoma plus pars tensa collapse. Otitis externa may also present with these symptoms but cholesteatoma is much more serious and should not be overlooked if a patient presents to a doctor with ear discharge and hearing loss the.
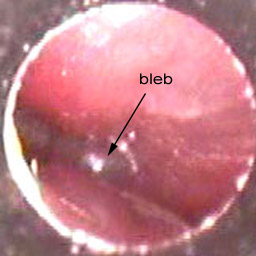
There is an attic retraction. 5 status post tubulation there is a ventilating tube located in the anterior inferior quadrant. Hard dry keratin debris in a small attic defect probable developing attic cholesteatoma. The defect in the ear drum is seen and indicated with the black arrow.
Recurrent cholesteatoma after closed techniques occurs in four patterns.