Elastic Band Force Extension Graph

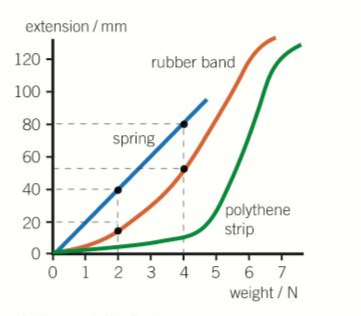
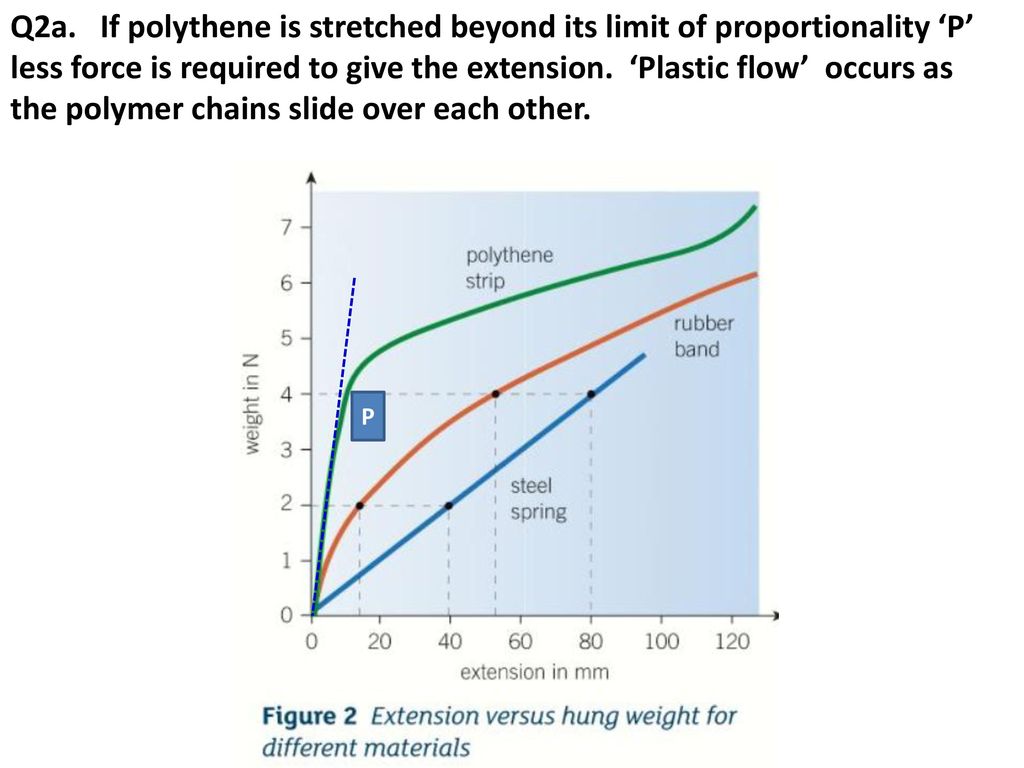
Non linear extension and plastic.
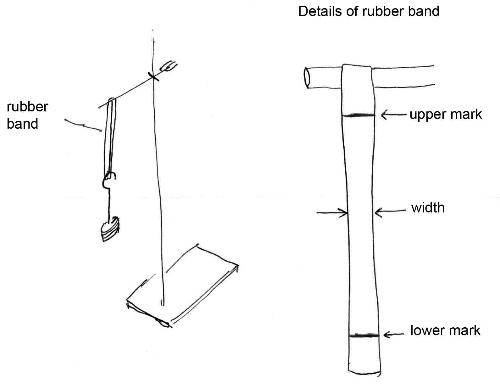
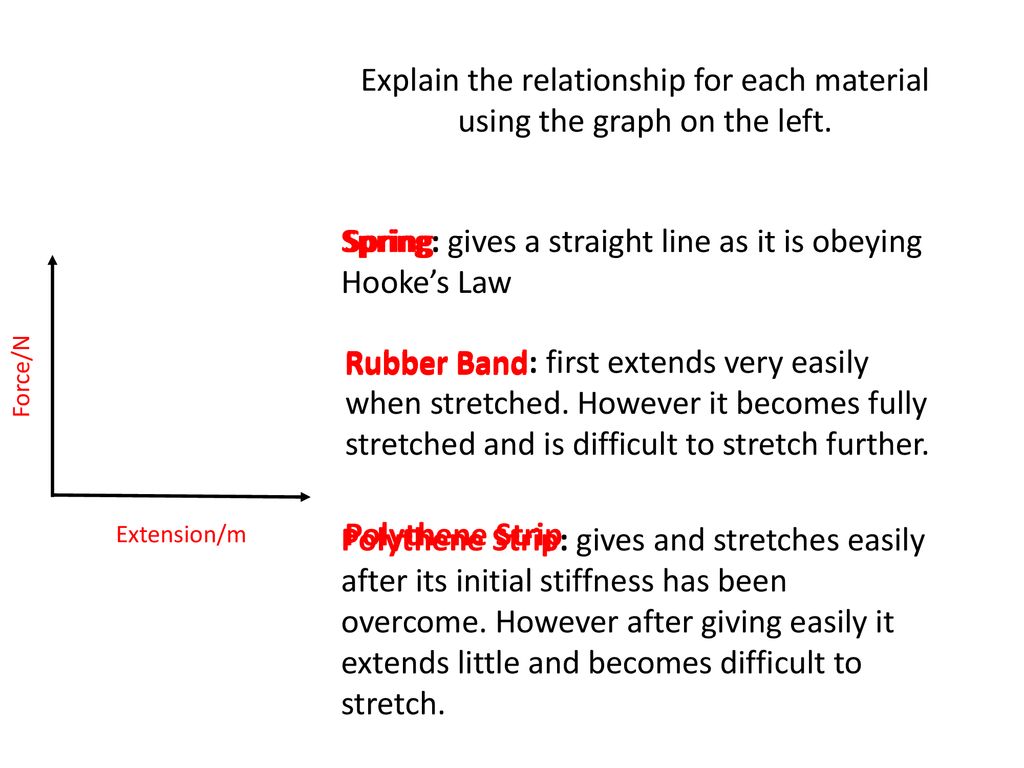
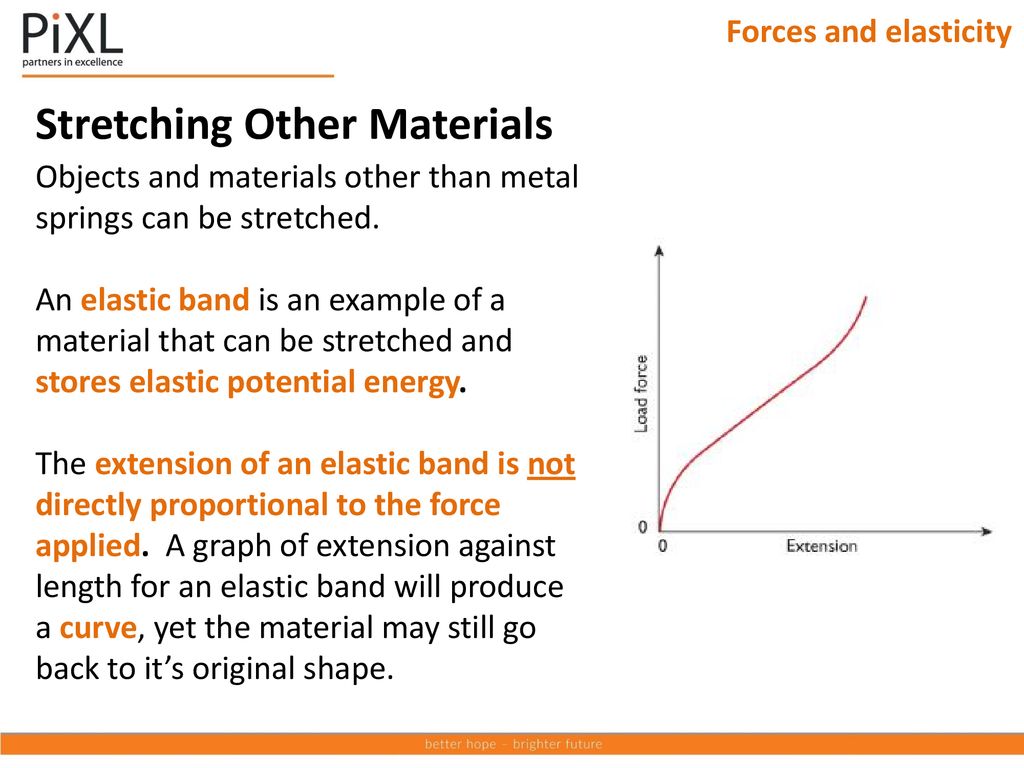
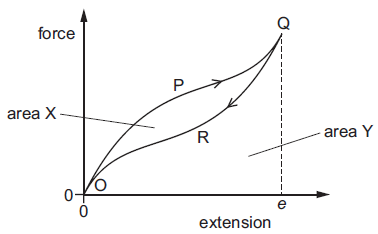
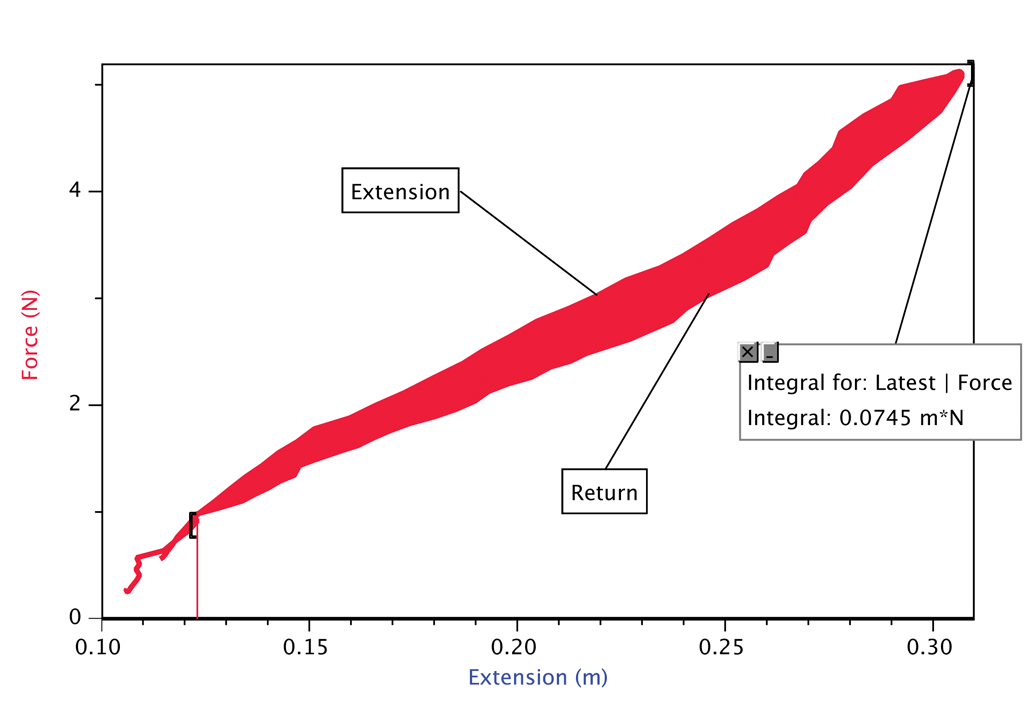
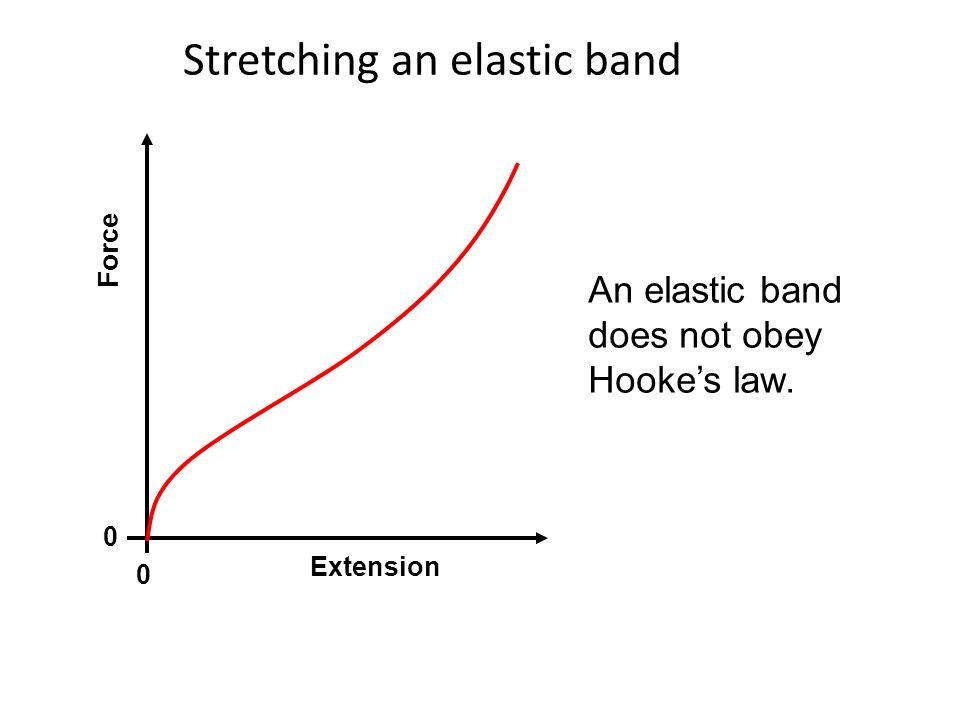
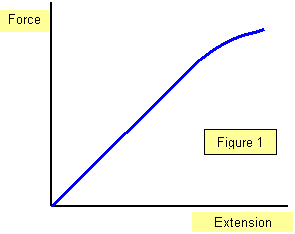
Elastic band force extension graph. The variables of the equation are. Deformation can be seen above the elastic limit. It will be easier to compress this rubber then expand it ii. Of a material or a spring is its increase in length when pulled.
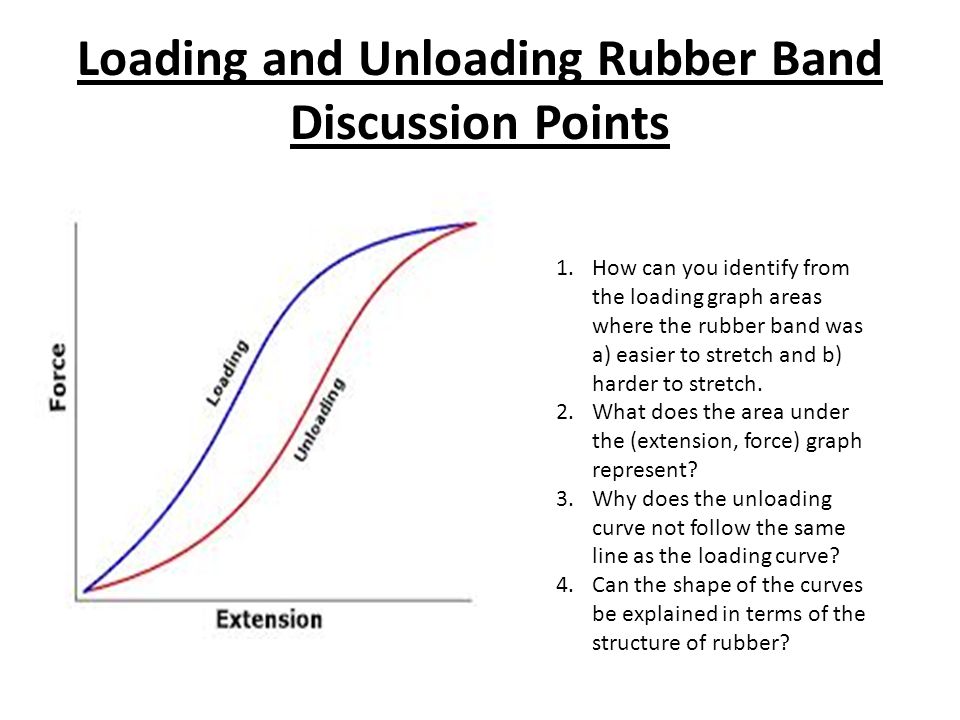
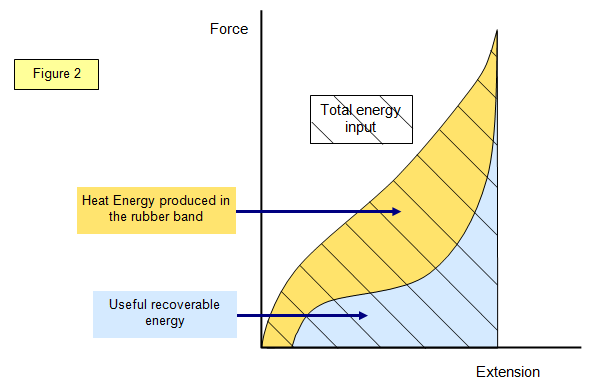
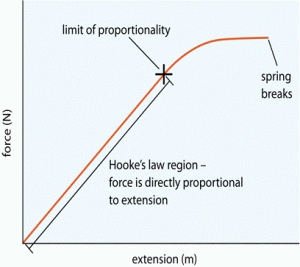
If you repeatedly stretch and release a rubber band you can feel the effect of heating caused by hysteresis. This works until the limit of proportionality is exceeded. The gradient of a force extension graph before the elastic limit is equal to the spring constant. The graph shows the behaviour of a length of wire in the region for which the substance obeys hook s law.
This works until the limit of proportionality is exceeded. To the force applied. For example if the force is doubled the extension doubles. P and q represent a p applied force q extension b p extension q applied force c p extension q stored elastic energy d p stored elastic energy q extension.
Rubber does not return to its original length after it is stretched iii. The minus sign shows that this force is in the opposite direction of the force that s stretching or compressing the spring. For example if the force is doubled the extension doubles. Click here to get an answer to your question the diagram shows a force extension graph for a rubber band.
Hooke s law says that the extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied to it. When an elastic object is stretched beyond its limit. F which represents force k which is called the spring constant and measures how stiff and strong the spring is and x is the distance the spring is stretched or compressed away from its equilibrium or rest position. Consider the following statements.
The rubber band will get heated if it is stretched and released which of these can be deduced from the graph.










_S01_066_Q01.png)